Collections工具类
集合框架中一个重要的类,其实是Collection接口的伴随类,其中定义了许多实用方法,用来获取集合视图,或提供一些方便的操作集合元素的算法。
由于视图是直接封装的Collection接口,因此其方法有些局限,并且由于特殊的设计,部分操作是不允许的(会抛出 UnsupportedOperationExceptin )。
不可修改视图 #
顾名思义,一旦获取,其内容不再可以修改,Java集合框架中可以用于获取的不可修改视图有:
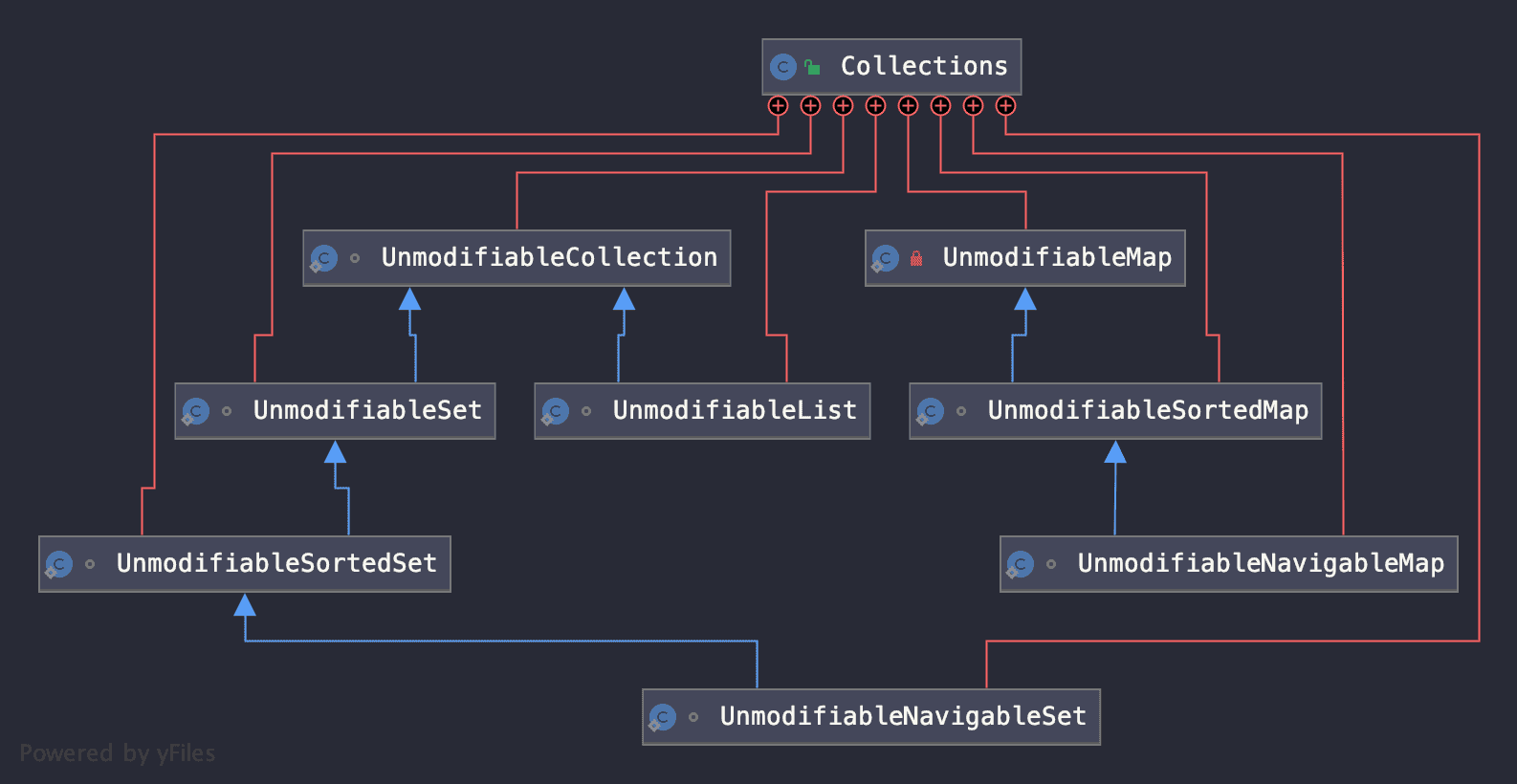
Collections通过静态方法获取的8个不可修改视图
Java中提供的获取不可修改视图的方法,只能用来遍历原集合中的信息,无法通过任何手段(集合,迭代器,entry等)修改集合,例如,当调用add方法时,Java的处理方式就是抛出 UnsupportedOperationException 异常:
1public class UnmodifiableViewTest {
2 static List<String> l = new ArrayList<String>() {{
3 add("fan");
4 add("bar");
5 add("foo");
6 add("anchor");
7 add("ripe");
8 add("rope");
9 add("hope");
10 }};
11 static Set<String> s = new HashSet<>(l);
12 static Map<String, String> m = new HashMap<String, String>() {{
13 put("c", "cable");
14 put("b", "bar");
15 put("f", "floyd");
16 put("e", "echo");
17 put("a", "anchor");
18 put("d", "dribble");
19 }};
20
21 public static void main(String[] args) {
22// unmodifiableList();
23// unmodifiableSet();
24 unmodifiableMap();
25 }
26
27 static void unmodifiableList() {
28 List<String> ul = Collections.unmodifiableList(l);
29 // 对视图集的元素增删会抛出UnsupportedOperationException
30 // strings.add("add");
31 // strings.remove("bar");
32 // strings.removeAll(l);
33 ul.forEach(System.out::print);
34 //可以操作迭代器
35 ListIterator<String> iterator = ul.listIterator();
36 System.out.println(iterator.nextIndex());
37// List<String> ul_sub = l.subList(1, 3);
38 List<String> ul_sub = ul.subList(1, 3);
39 // 子集对元素的操作也是不支持的
40// ul_sub.removeIf(s -> s.equals("foo"));
41 ul_sub.forEach(System.out::println);
42 }
43
44 static void unmodifiableSet() {
45 Set<String> set = Collections.unmodifiableSet(s);
46 System.out.println(set.contains("anchor"));
47 Iterator<String> i = set.iterator();
48 i.next();
49 // 迭代器无法移除元素是必然的
50 // i.remove();
51 // set.clear();
52 TreeSet<String> ts = new TreeSet<>(s);
53 // 使用sorted set构建
54 NavigableSet<String> ns = Collections.unmodifiableNavigableSet(ts);
55 // 无法从集中移除元素 UnsupportedOperationException
56// String s = ns.pollFirst();
57 System.out.println(ns.first());
58 NavigableSet<String> anchor = ns.headSet("anchor", true);
59 // 子集也不能被修改
60// anchor.remove("anchor");
61 anchor.forEach(System.out::println);
62 }
63
64 static void unmodifiableMap() {
65 Map<String, String> map = Collections.unmodifiableMap(m);
66 // 不支持的操作
67 // map.replace("a","apple");
68 Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> e = map.entrySet();
69 System.out.println(map.get("f"));
70
71 TreeMap<String, String> tm = new TreeMap<>(m);
72 // 使用sorted map
73 NavigableMap<String, String> nm =
74 Collections.unmodifiableNavigableMap(tm);
75 System.out.println(nm.ceilingEntry("car").getValue());
76 NavigableMap<String, String> sm = nm.subMap("b", true, "d", true);
77 // 不支持的操作
78 // sm.remove("c");
79 sm.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(k + ", " + v));
80 NavigableMap<String, String> descendingMap = sm.descendingMap();
81 descendingMap.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(k + ", " + v));
82 }
83}
稍微查看源码就知道,不可修改视图的工作方式:
1 static class UnmodifiableList<E> extends UnmodifiableCollection<E>
2 implements List<E>
3 {
4 //...
5 public E get(int index) {return list.get(index);}
6 public E set(int index, E element) {
7 throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
8 }
9 public void add(int index, E element) {
10 throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
11 }
12 public E remove(int index) {
13 throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
14 }
15 //...
16 }
不可修改视图的封装思路就是,当试图改变集合时,不予处理并抛出异常。
同步视图 #
由于Java集合框架中的组成都不是同步的(Vector和Hashtable除外), Java SE 8 API Specification 里面重复出现的一段话就是:
Note that this implementation is not synchronized. If multiple threads access an
ArrayListinstance concurrently, and at least one of the threads modifies the list structurally, it must be synchronized externally. (A structural modification is any operation that adds or deletes one or more elements, or explicitly resizes the backing array; merely setting the value of an element is not a structural modification.) This is typically accomplished by synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the list. If no such object exists, the list should be "wrapped" using theCollections.synchronizedListmethod. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental unsynchronized access to the list:List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(...));
因此同步视图就是用来处理并发访问的,除了同步视图之外,java.util.concurrent包里提供了线程安全的集合,用于并发环境。
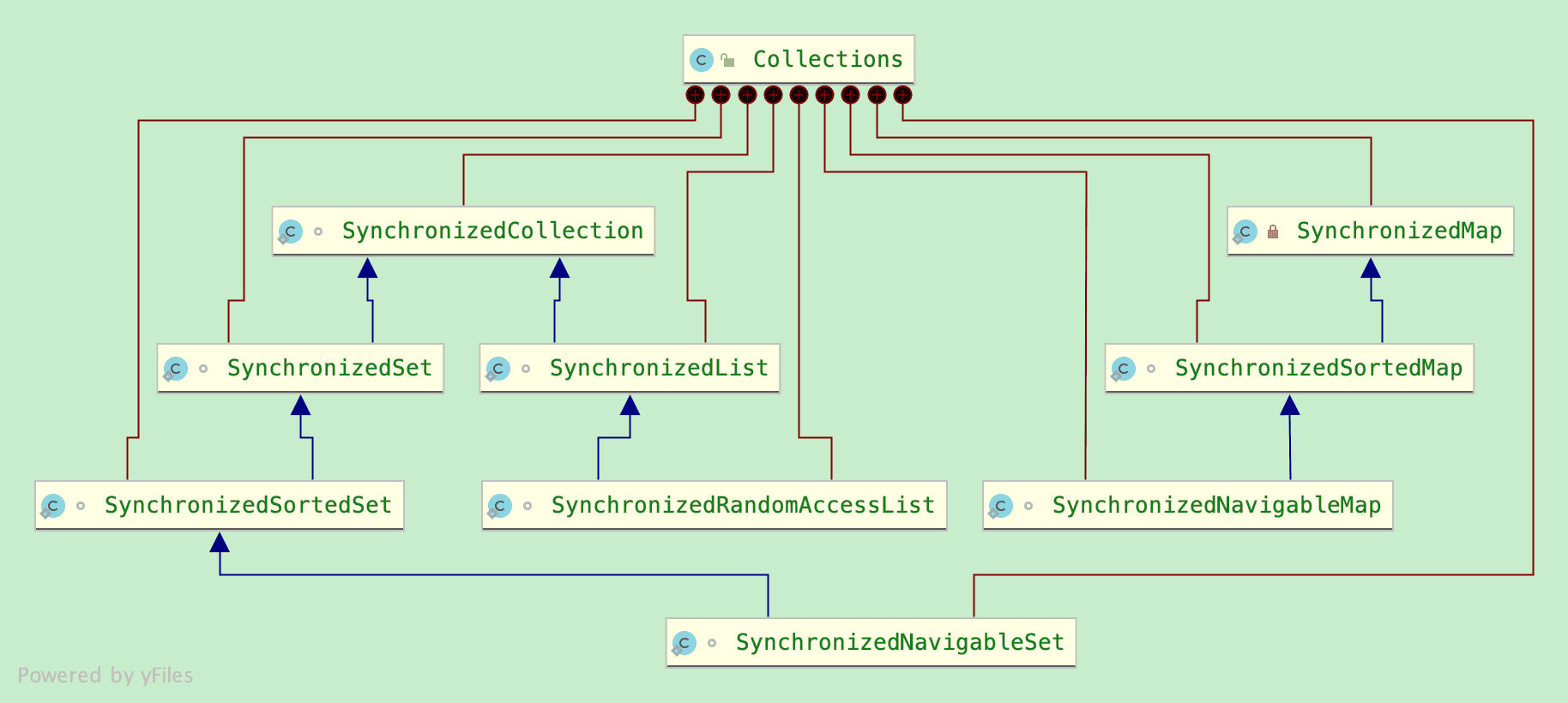
Collections通过静态方法获取的8个同步视图(不包含SynchronizedRandomAccessList)
受查视图 #
受查视图用来对泛型类发生问题时提供调试支持。
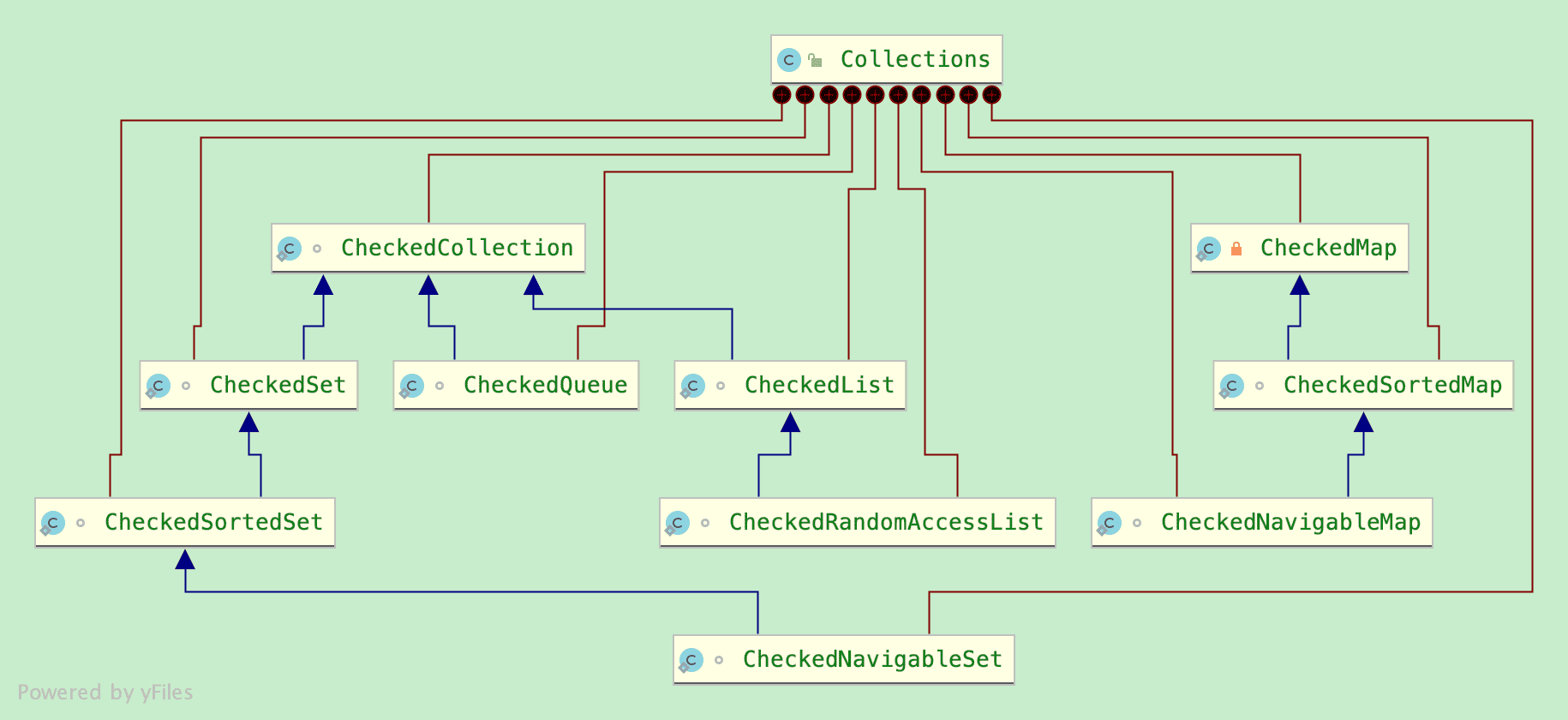
Collections通过静态方法获取的9个受查视图(不包含checkededRandomAccessList)
实用方法 #
空集 #
Collections提供了一些返回空集合、映射、迭代器的方法,实际上返回的是Collections所封装的对应的对象。
向返回的空集合中插入元素会抛出 UnsupportedOperationException。
1static void emptyList(){
2 List<Object> emptyList = Collections.emptyList();
3 //emptyList.add(1); // USOE
4 System.out.println(emptyList.size()); // actual 0
5}
单一元素集合 #
Collections还提供了返回指定1个元素的集合或映射:
1static void singletonList(){
2 Set<String> singlton = Collections.singleton("singlton");
3 System.out.println(singlton.size()); // actual 1
4 // singlton.add("sin"); // USOE
5 // singlton.clear(); // USOE
6}
同样地,单一元素集合也是不可修改的。
其他有利算法 #
Collections类还包含了很多有利的算法,如:
Collections.sort(List<T>)
根据对集合元素按照自然顺序升序排序,而
Collections.binarySearch(List<? extends Comparable<? super T>> list, T key)
会二分查找集合中的元素,其前提是元素是自然升序排序的1
除此之外,Collections还定义了一些实用方法,简单列出部分:
public static void reverse(List<?> list)
public static void shuffle(List<?> list)
public static void shuffle(List<?> list, Random rnd)
public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T min(Collection<? extends T> coll)
public static <T> T min(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp)
public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll)
public static <T> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp)
排序和查找有重载方法,具体请查看API文档 ↩︎