HashMap和TreeMap
由于Map的键是Set,因此使用可变对象作为Map的key时,需要覆盖 equals 和 hashCode 方法,Map不能使用自身作为key。
Java 8对Map接口进行了优化,新增了主要是针对函数式接口的 默认 方法(方法体被省略):
default V merge (K key, V value,
BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {...}
default V compute (K key,
BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {...}
default V computeIfPresent (K key,
BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {...}
default V computeIfAbsent (K key,
Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {...}
default V replace (K key, V value) {...}
default boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {...}
default boolean remove (Object key, Object value) {...}
default V putIfAbsent (K key, V value) {...}
default void replaceAll (
BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {...}
default V getOrDefault (Object key, V defaultValue) {...}
上述方法使用的不多,主要用来对Map键值进行更新,按需查阅API文档。
HashMap #
HashMap是由散列表对键进行散列的,允许null键和null值。HashMap是无序的,这点和HashSet是一样的
HashMap和Hashtable大致相同,区别在与Hashtable是同步的,且Hashtable不允许null
HashMap的初始化和扩容机制叙述参见 散列表,如果初始化时不指定容量(桶数?容量不是键值对数目),默认为16。容量总是2n,最大容量是230,每次扩容加倍,当桶数大于最大桶数后,不再rehash。容量总是为2的幂次的原理和 ArrayDeque一致,通过5次位运算将低位全部转为1,然后执行+1操作进位,变成下一个2n。因此HashMap带参构造器指定的capacity最后会初始化为大于其的最近的2n(1变2,3变4,5变8,9变16...)。
HashMap使用table和entrySet分别表示桶数和当前映射中的键值对数:
transient Node<K,V>[] table; 桶数组,桶由链表构成;
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; 映射中的键值对数,size
int threshold;
临界键值对数,等于 table.length * loadFactor,当size > threshold时,触发扩容
final float loadFactor; 装载因子,默认0.75
1static void bucketsTest() throws Exception {
2 //load factor 0.75
3 HashMap<String, String> hm = new HashMap<>(7);
4 hm.put("1", "ok");
5 hm.put("2", "fine");
6 hm.put("3", "nice");
7 hm.put("4", "no");
8 hm.put("5", "ops");
9 hm.put("6", "fuck");
10
11 Class<?> cls = HashMap.class;
12
13 Field table = cls.getDeclaredField("table");
14 Field threshold = cls.getDeclaredField("threshold");
15 // can not access
16 // Class<?> node = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");
17 table.setAccessible(true);
18 threshold.setAccessible(true);
19 // Node<K,V>[]
20 Object[] o = (Object[]) table.get(hm);
21 System.out.println("initial buckets size: " + o.length);
22 System.out.println("initial threshold: " + threshold.get(hm));
23
24 Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = hm.entrySet();
25 System.out.println("number of entries: " + entries.size());
26 // 遍历
27 /*entries.forEach((e) -> {
28 System.out.println(e.getKey() + e.getValue());
29 });*/
30 hm.put("apple", "music");
31 // reshash needed
32 System.out.println(("buckets after rehash: "
33 + ((Object[]) table.get(hm)).length));
34}
35/* output:
36initial buckets size: 8
37initial threshold: 6
38number of entries: 6
39buckets after rehash: 16
40*///:~
上例证实了HashMap的扩容过程,当映射中的元素数大于桶数与装载因子之积时,便会扩容。
Map中提供3种集合视图,键的,值的和entry的,视图并不能对映射进行完全结构性控制,比如向Map中添加条目,则只能使用Map.put方法,使用视图时,除了删除这一改变Map结构的操作,其他操作会抛出UnsurportedOperationException。
HashMap的集合视图都支持迭代器,并可以通过任意视图的迭代器删除键值对,但是不支持新增和替换键值对。
1private static void viewTest() {
2 Map<Integer, String> hm = new HashMap<>(8);
3 hm.put(1,"难忘的一天");
4 Set<Integer> keySet = hm.keySet();
5 //keySet.add(2); // unsupported operation exception
6 Iterator<Integer> ikey = keySet.iterator();
7 ikey.next();
8 // can remove key-value pair by keySet
9 ikey.remove();
10 ikey.forEachRemaining(System.out::println);
11
12 Collection<String> values = hm.values();
13 // already deleted
14 System.out.println("values contains: " + values.contains("难忘的一天"));
15 // values.add("你瞒我瞒"); // unsupported either
16 hm.put(1,"你瞒我瞒");
17 hm.put(2,"樱花树下");
18 // ikey.next(); // fast-fail iterator, ikey is out of date
19 boolean remove = values.remove("你瞒我瞒");
20 Iterator<String> ivalue = values.iterator();
21 ivalue.next();
22 ivalue.remove();
23
24 hm.put(1,"红豆");
25 hm.put(2,"风衣");
26 Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries = hm.entrySet();
27 // entries.add() // unsupported either
28 System.out.println("entry size: " + entries.size());
29 // remove entry with particular key-value
30 entries.remove(new Map.Entry<Integer, String>() {
31 @Override
32 public Integer getKey() {
33 return 1;
34 }
35 @Override
36 public String getValue() {
37 return "红豆";
38 }
39 @Override
40 public String setValue(String value) {
41 return null;
42 }
43 });
44 hm.forEach((k,v) -> System.out.println("key:" + k + ", value:" + v));
45 Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> ientry = entries.iterator();
46 ientry.next();
47 ientry.remove();
48 ientry.forEachRemaining(System.out::println);
49}
50/* output
51values contains: false
52entry size: 2
53key: 2, value:风衣
54*///:~
值得一提的事,和
SortedSet的子集视图一样,对原集合和视图的修改是相互的,不会引发 ConcurrentModificationException ,但是其对映射的操作是有限的,比如keySet.add(2)就抛出 UnsupportedOperationException ,迭代器不支持操作。查看源码即可知:
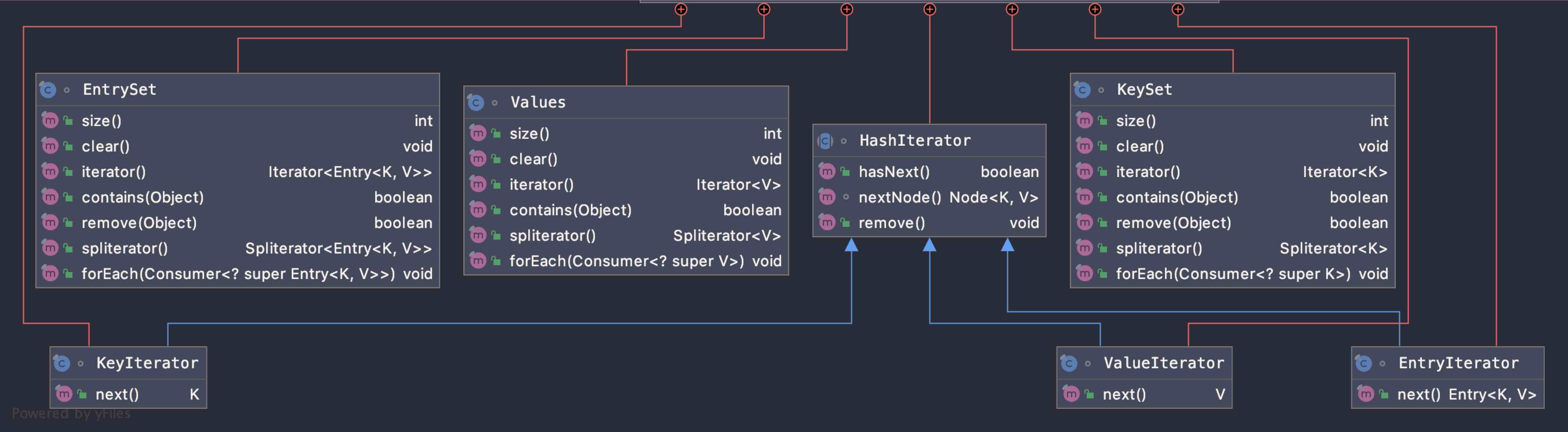
HashMap内部视图和迭代器方法表
可以看到,视图实现的方法有限,并没有实现集合的所有方法。因此当使用视图调用add()方法时,直接在AbstractCollection里抛出异常:
1public boolean add(E e) {
2 throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
3}
TreeMap #
TreeSet是TreeMap的KeySet的封装,TreeMap是使用红—黑树对键进行排序的有序映射。
TreeMap的继承结构和TreeSet极为相似,对应地,TreeMap是SortedMap和NavigableMap的实现,SortedMap/NavigableMap的接口声明和SortedSet/NavgableSet相似,所声明的方法名都是自解释型的,具体可查看JDK文档。
要将条目插入TreeMap中,key必须是可排序的,排序方式可以是自然排序或者定义比较器,和TreeSet一样,比较器规则必须和equals方法的结果保持一致,以避免映射中出现重复key-value。
TreeMap的集合视图和对应的迭代器表现和HashMap一致。
- 视图和映射的作用是相互的,即修改映射,视图随之修改,反之亦然,但是视图支持的操作是有限的,注意 UnsupportedOperationException;
- 迭代器是 fail-fast 的, 只支持remove一个改变映射结构的方法;
1static {
2 map.put("hebe", "不醉不会");
3 map.put("AMIT","母系社会");
4 map.put("Lin","可惜没如果");
5 map.put("andy", "一起走过的日子");
6 map.put("lala", "寻人启事");
7 map.put("yoga", "说谎");
8}
9static void treeMapTest() {
10 Map<String, String> tm = new TreeMap<>(map);
11 Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = tm.entrySet();
12 tm.put("andy", "来生缘"); // 映射和entrySet是互相作用的
13 for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) {
14 entry.setValue("难搞");
15 break;
16 }
17 tm.computeIfPresent("lala", (k, v) -> "失落沙洲");
18 // Unsupported Operation Exception
19 // entries.add(new Map.Entry<String, String>() {...});
20 tm.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(k + ": " + v));
21
22 // test iterator
23 Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> ie = entries.iterator();
24 ie.next();
25 ie.remove();
26 // tm.putAll(map); //ConcurrentModificationException
27 ie.next();
28 ie.forEachRemaining(x -> System.out.print(x + "\t"));
29 // 指定比较器
30 Map<String, String> tm2 = new TreeMap<>(String::compareToIgnoreCase);
31 tm2.putAll(map);
32 System.out.println();
33 tm2.forEach((k,v)-> System.out.println(k +": " + v));
34}
35/* output:
36AMIT: 难搞
37Lin: 可惜没如果
38andy: 来生缘
39hebe: 不醉不会
40lala: 失落沙洲
41yoga: 说谎
42andy=来生缘 hebe=不醉不会 lala=失落沙洲 yoga=说谎
43AMIT: 母系社会
44andy: 一起走过的日子
45hebe: 不醉不会
46lala: 寻人启事
47Lin: 可惜没如果
48yoga: 说谎
49*///:~
上例中分别对HashMap使用自然排序和指定比较器的方法,可以看到映射中key的排序差异。
当指定TreeMap实现类的名字SortedMap或NavigableMap的实现时,方可使用SortedMap和NavigableMap的实用方法,由于方法名都是解释型的,此处不多作表述:
1 static void navigableTest() {
2 TreeMap<String, String> tm = new TreeMap<>(map);
3 System.out.println(tm.firstEntry().getKey());
4 // 使用一个比key 'andy'大的值,即可包含这个key,"+ 0"是一个实用手段
5 SortedMap<String, String> subMap = tm.subMap("AMIT", "andy" + "0");
6 subMap.compute("AMIT", (k, v) -> "彩虹");
7 subMap.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(k + ", " + v));
8
9 //NavigableMap接口方法,返回大于或等于给定key的一个entry
10 System.out.println(tm.ceilingEntry("AMIT").getValue());
11 }
12/* output:
13AMIT
14AMIT, 彩虹
15Lin, 可惜没如果
16andy, 一起走过的日子
17彩虹
18*///:~
由于
subMap方法是“包前不包尾”的(其他获取子映射视图的方法也一样),为了包尾,可以使用上例的方法。
NavigableMap对获取子映射视图的方法进行了扩展,不作过多表述。