Queue
Queue(队列),实际开发过程中,在单线程环境下使用的并不多,Queue作为集合框架中重要组成似乎习惯性被忽略。队列总是先持有元素,再处理元素1。
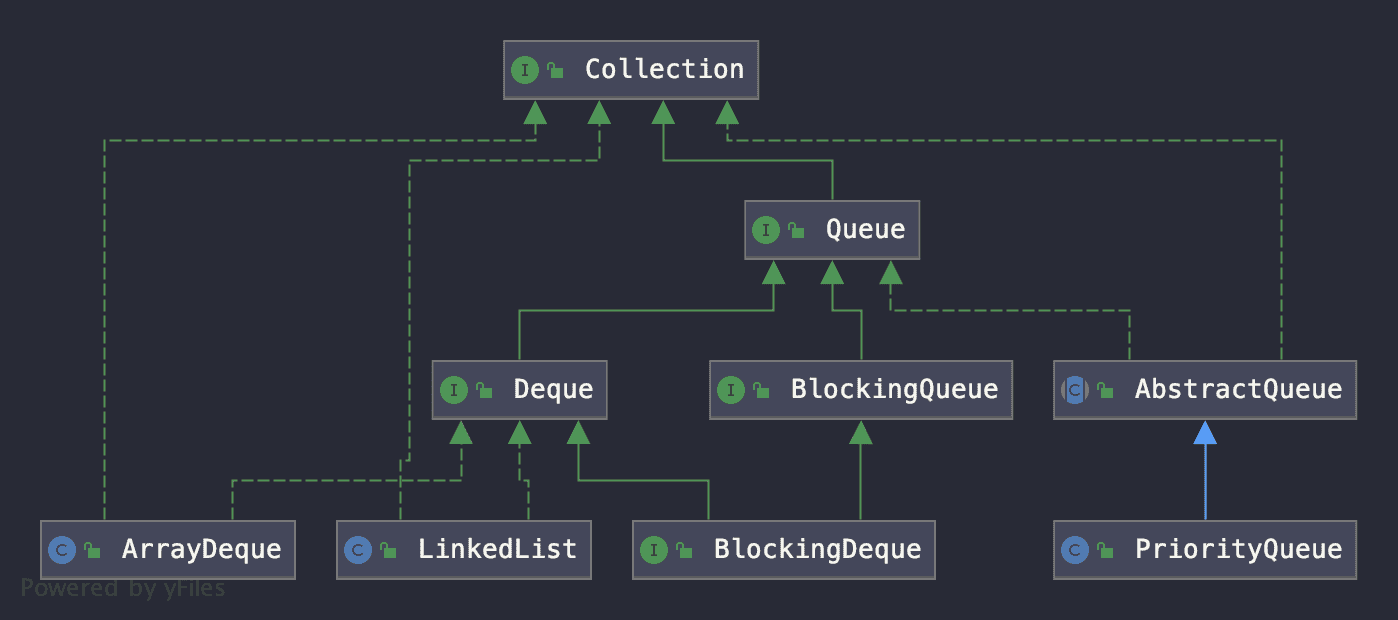
Queue继承关系简图
除了Collection定义的操作之外,Queue定义了额外的插入/删除/检查元素的操作,这些操作有2种形式:
| Throws Exception | Returns special value | |
|---|---|---|
| Insert | add(e) | offer(e) |
| Remove | remove() | poll() |
| Examine | element() | peek() |
如表所示,add/remove/element方法失败后抛出异常。offer/poll/peek方法失败后返回一个特殊值(null或false,视具体操作不同),需要说明的是,offer()方法主要是为有容量限制的队列设计的offer()方法比add()方法更可取。
典型的队列遵从FIFO( first-in-first-out )原则,FIFO队列的新元素总是插入到队尾。
当然有例外,PriorityQueue 就是之一,它根据给定(或默认)的比较器决定元素顺序;此外还有LIFO( last-in-first-out )队列(如栈)。
不管是何种队列,都可以使用remove()或poll()移除并返回 队列头元素,至于头元素是“谁”就由队列的排序规则决定。此二者的区别体现在当队列为空时,remove()抛出异常,而poll()返回null。
element()和peek()获取但不移除 队列头元素,区别在于当队列为空时,element()抛出异常,而peek()返回null。
offer()方法尝试向队列中插入一个元素,否则返回false,而Collection.add方法失败之后会抛出(运行时)异常。因此offer()方法适用于定容或有界队列中插入元素。
队列中不允许插入null,或者说不应将null插入队列中(LinkedList允许空值),因为null会作为队列方法的特殊返回值(空队列指示器)出现,若将null插入队列,会引发歧义。
Queue有两个子接口:
BlockingQueue
Queue中并没有定义 阻塞队列 的相关方法,阻塞队列通常在 并发编程 中使用。阻塞队列的方法会等待元素出现或(有限)集合空间可用这2个条件之一满足才执行。
Deque
双端队列 是支持从 队首和队尾添加/删除元素 的线性集合,一般来说,
Deque没有容量限制,但是其也支持有限长度的实现。从
Deque的定义可知,其比Queue的定义多了队头的入队、队尾的出队以及相应的查看操作:First Element (Head) Last Element (Tail) Throws exception Special value Throws exception Special value Insert addFirst(e) offerFirst(e) addLast(e) offerLast(e) Remove removeFirst() pollFirst() removeLast() pollLast() Examine getFirst() peekFirst() getLast() peekLast() 与
Queue不同的是,获取而不删除的方法由element()变成了getXXX(),这些方法用来在队列头/尾中插入/删除/检查元素,当操作失败时有不同的处理:一组直接抛出异常,一组返回一个特殊值(null或false)。同样地,返回特殊值的方法适用于有限容量的队列。由于
Deque继承自Queue,当其作为Queue使用时,是一个FIFO队列,新元素会添加至队尾,删除操作删除队首元素,因此下表的方法在Deque作为Queue使用时是等价的:Queue Methods Equivalent Deque Methods add(e) addLast(e) offer(e) offerLast(e) remove() removeFirst() poll() pollFirst() element() getFirst() peek() peekFirst() 此外,Deque还可以作为LIFO队列(栈)使用,当作为栈使用时,新元素会从队首添加或删除,这种情况下,
java.util.Stack的方法和Deque的方法是等价的:Stack Methods Equivalent Deque Methods push(e) addFirst(e) pop() removeFirst() peek() peekFirst() ArrayDeque
就是一个LIFO队列实现可以用作LIFO队列
Deque不提供使用索引操作集合的方法。
和Queue一样,虽然没有严格约束不能插入null到队列中,也强烈不推荐将null值插入。
除此之外,Deque还提供2个删除元素的方法:
boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o);
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o);
PriorityQueue #
优先级队列不允许null值。
优先级队列是一个有序队列,其底层是由堆( heap )实现的,堆是一个可以自我调整的二叉树。优先级队列的排序依据可以来自元素的自然排序(实现Comparable接口)或自定义比较器,当使用自然排序规则时,优先级队列不允许插入non-comparable对象。
优先级队列的第一个元素(head)总是按照排序规则计算出最小元素,如果有几个相等的最小元素,那么head为其中任意一个,当使用poll()或remove()后,其他最小元素自动移动至head。
从输出来看,优先级队列并没有对所有元素进行完全排序,而是队列发生结构性变化时,保证队头元素一定是满足排序规则的最小元素。
优先级队列是自动扩容的,其扩容机制为:
- 当队列较小时(<64),容量翻倍;
- 当队列长度>64时,容量增加一半(和
ArrayList一样)
优先级队列也有迭代器,此迭代器不能按照指定排序规则顺序迭代元素——优先级队列并没有对所有元素进行排序,若想获得所有元素的排序,可以使用Arrays.sort(pq.toArray())。
参考下例:
1static void unsorted(){
2 Queue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
3 pq.add(7);
4 pq.add(1);
5 pq.add(12);
6 pq.add(6);
7 pq.add(9);
8 pq.add(1);
9 System.out.println("pq: " + Arrays.toString(pq.toArray()));
10 Object[] array = pq.toArray();
11 Arrays.sort(array);
12 System.out.println("sorted array:" + Arrays.toString(array));
13 // the least element always in the head of queue
14 pq.poll();
15 pq.forEach((e) ->{
16 System.out.print(e + "\t");
17 });
18}
19/* output:
20pq: [1, 6, 1, 7, 9, 12]
21sorted array:[1, 1, 6, 7, 9, 12]
221 6 12 7 9
23*///:~
和上面的叙述一样,PriorityQueue并没有对所有元素进行排序,不过其保证了最小元素始终在队首,并且队列发生结构性变化时,队列中的元素“位置”也会发生变化。
下例展示了如何在PriorityQueue中使用自定义比较器:
1static void userComparator() {
2 class PC {
3 private String model;
4 private Double price;
5
6 private PC(String model, Double price) {
7 this.model = model;
8 this.price = price;
9 }
10 }
11
12 // compare by price descend
13 Queue<PC> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> (int) (o2.price - o1.price));
14 pq.add(new PC("dell", 15499d));
15 pq.add(new PC("apple", 18899d));
16 pq.add(new PC("samsung", 8999d));
17 pq.add(new PC("asus", 12999d));
18 pq.add(new PC("hp", 6399d));
19 pq.add(new PC("lenovo", 16999d));
20
21 pq.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e.price + "\t"));
22 System.out.println();
23 pq.remove();
24 pq.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e.price + "\t"));
25 System.out.println();
26 pq.remove();
27 pq.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e.price + "\t"));
28 System.out.println();
29
30 // compare by model ascend
31 Queue<PC> pq1 = new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2) -> (o1.model.compareTo(o2.model)));
32 pq1.add(new PC("samsung", 8999d));
33 pq1.add(new PC("apple", 18899d));
34 pq1.add(new PC("lenovo", 16999d));
35 pq1.add(new PC("asus", 12999d));
36 pq1.add(new PC("dell", 15499d));
37 pq1.add(new PC("hp", 6399d));
38 pq1.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e.model + "\t"));
39 System.out.println();
40 pq1.remove();
41 pq1.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e.model + "\t"));
42 System.out.println();
43 pq1.remove();
44 pq1.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e.model + "\t"));
45}
46/* output:
4718899.0 15499.0 16999.0 12999.0 6399.0 8999.0
4816999.0 15499.0 8999.0 12999.0 6399.0
4915499.0 12999.0 8999.0 6399.0
50apple asus hp samsung dell lenovo
51asus dell hp samsung lenovo
52dell lenovo hp samsung
53*///:~
从结果来看,元素在PriorityQueue里并不是全排序的,不过其会自动将“最小”的元素移动至队首。
此例中,如果不在构造器中指定比较器,PriorityQueue会在运行时抛出 ClassCastException——试图将PC向上转型为Comparable时异常。
LinkedList #
LinkedList是Deque的实现,可以作为双端队列使用,其实现了Deque声明的所有方法。
想将LinkedList作为Deque使用,须将其声明为 Deque:
1Deque<String> deque = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList得益于双向链表节点的灵活性,很容易就能够实现在首尾两端对元素进行操作。
ArrayDeque #
ArrayDeque是由循环数组实现的双端队列,没有容量限制,并且能够自动扩容,不允许 插入null值。
ArrayDeque作为栈( LIFO 队列)使用时,效率比java.util.Stack高。
ArrayDeque作为Queue使用时,效率比LinkedList高。
ArrayDeque的迭代器也是 fail-fast 的,意味着和ArrayList一样,在获取迭代器之后使用集合方法对队列进行结构性修改会引发 ConcurrentModificationException。
ArrayDeque主要的字段域有:
1transient Object[] elements;
2transient int head;
3transient int tail;
4private static final int MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8;
elements用于存储数据,head和tail分别用来标记队列的头尾。 MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY 是创列的最小容量(23)。当构造器没有指定容量时,初始化容量为16;只有当指定容量且数值小于8时才会使用8作为初始容量。
参考如下源码:
1// ArrayDeque初始化时容量的计算
2private static int calculateSize(int numElements) {
3 int initialCapacity = MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
4 // Find the best power of two to hold elements.
5 // Tests "<=" because arrays aren't kept full.
6 if (numElements >= initialCapacity) {
7 initialCapacity = numElements;
8 initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 1);
9 initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 2);
10 initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 4);
11 initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 8);
12 initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 16);
13 initialCapacity++;
14
15 if (initialCapacity < 0) // Too many elements, must back off
16 initialCapacity >>>= 1;// Good luck allocating 2 ^ 30 elements
17 }
18 return initialCapacity;
19}
若指定容量>8时,那么需要对其进行 5次右移及位或运算保证最终的容量大小是2n,比如传进来的参数是13,那么最后得到的容量就是24。
ArrayDeque中,当head==tail2时触发扩容,容量增加一倍。
TODO
参考如下源码:
1public void addFirst(E e) {
2 //...
3 if (head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1) == tail)
4 doubleCapacity();
5 //...
6}
7public void addLast(E e) {
8 //...
9 if (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1) == head)
10 doubleCapacity();
11 //...
12}
13public E pollFirst() {
14 //...
15 if (head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1) == tail)
16 doubleCapacity();
17 //...
18}
19public E pollLast() {
20 //...
21 if (tail = (tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1) == head)
22 doubleCapacity();
23 //...
24}
25// 扩容
26private void doubleCapacity() {
27 assert head == tail;
28 int p = head;
29 int n = elements.length;
30 int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
31 int newCapacity = n << 1;
32 if (newCapacity < 0)
33 throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
34 Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
35 System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r);
36 System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p);
37 elements = a;
38 head = 0;
39 tail = n;
40}
一般地,循环队列都是使用模运算实现的,而ArrayDeque通过位运算来实现循环队列,Java集合框架中很多地方都使用了位运算(如HashMap的扩容),位运算和模运算有
如下关系:
x % 2n = x & (2n - 1)
并且位运算的效率远远高出模运算,这就是Java设计的高明之处。
当触发扩容时,将容量增加一倍,同时使用两次System.arraycopy将原数组拷贝到新数组中,现引用
ArrayDeque扩容将其机制作简要阐述:
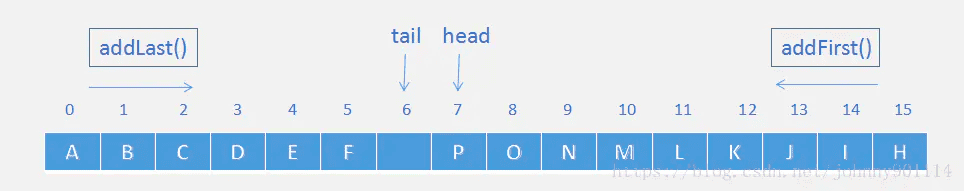
假如默认容量16,此时数组情况如图
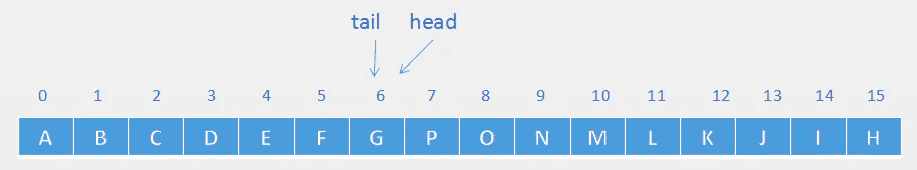
当再次调用
addFirst("G")时,
此时
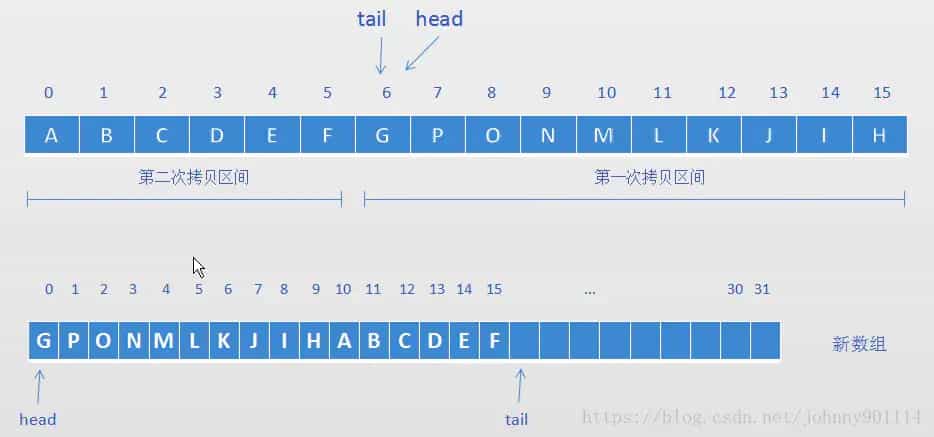
head==tail,触发扩容,将会创建一个大小为 16*2 的新数组,然后通过两次拷贝将原数组的数据复制到新数组
- 第一次将G-H拷贝到新数组
- 第二次将A-F拷贝到新数组
ArrayDeque扩容图解 来源见水印
参考如下示例:
1void initializationTest() throws Exception {
2 Deque<Integer> aq = new ArrayDeque<>(5);
3 // actual circle array size: 8
4 System.out.println("array size : " + getElements(aq).length);
5 // double capacity while i = 7
6 for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
7 aq.offerLast(i);
8 }
9 Object[] elements = getElements(aq);
10 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(elements));
11 aq.addLast(19);
12 aq.forEach(e-> System.out.print(e + "\t"));
13}
14
15private <T> T[] getElements(Deque<?> aq) throws Exception {
16 Class<?> cls = ArrayDeque.class;
17 Field ef = cls.getDeclaredField("elements");
18 ef.setAccessible(true);
19 return (T[]) ef.get(aq);
20}
21/* output:
22array size : 8
23[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null]
240 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 19
25*///~
ArrayDeque的具体方法就不再赘述了,其囊括了作为Queue以及Stack的的实现。